
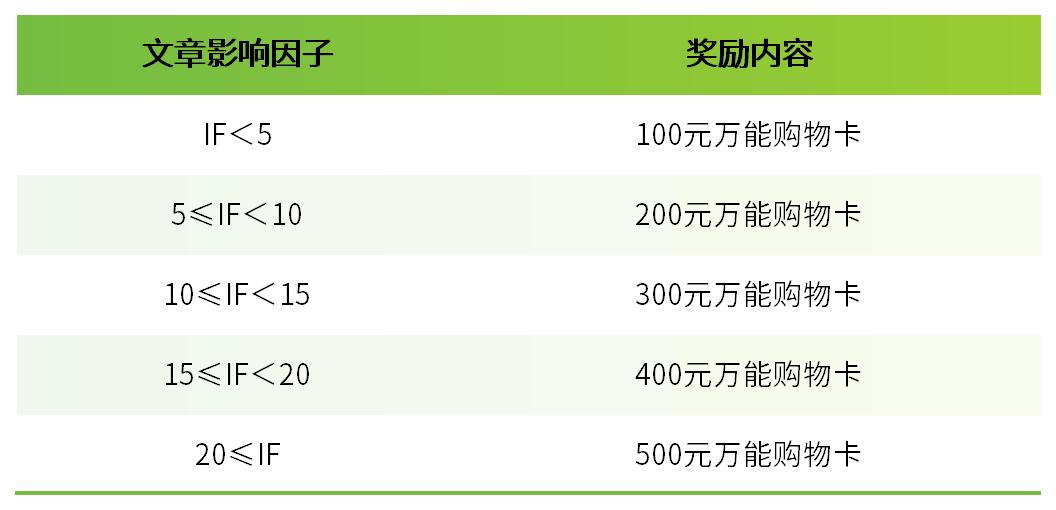
截止目前,引用Bioss產(chǎn)品發(fā)表的文獻(xiàn)共32,920篇,總影響因子161,928.42分,發(fā)表在Nature, Science, Cell以及Immunity等頂級期刊的文獻(xiàn)共124篇,合作單位覆蓋了清華、北大、復(fù)旦、華盛頓大學(xué)、麻省理工學(xué)院、東京大學(xué)以及紐約大學(xué)等國際知名研究機(jī)構(gòu)上百所。
我們每月收集引用Bioss產(chǎn)品發(fā)表的文獻(xiàn)。若您在當(dāng)月已發(fā)表SCI文章,但未被我公司收集,請致電Bioss,我們將贈(zèng)予現(xiàn)金鼓勵(lì),金額標(biāo)準(zhǔn)請參考“發(fā)文章 領(lǐng)獎(jiǎng)金”活動(dòng)頁面。
本文主要分享引用Bioss產(chǎn)品發(fā)表文章至Nature, European heart journal open, Nature Biotechnology, Molecular Cancer, Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, Cellular & Molecular Immunology, Nature Microbiology等期刊的9篇IF>20的文獻(xiàn)摘要,讓我們一起欣賞吧。
Nature [IF=50.5]

文獻(xiàn)引用產(chǎn)品:
bs-10197R-BF647 | nNOS Rabbit pAb, BF647 conjugated | Flow-Cyt
bs-33176M-BF647 | eNOS Mouse mAb, BF647 conjugated | Flow-Cyt作者單位:哥倫比亞大學(xué)瓦格洛斯醫(yī)學(xué)院
摘要:Stem cells reside in specialized microenvironments, termed niches, at several different locations in tissues. The differential functions of heterogeneous stem cells and niches are important given the increasing clinical applications of stem-cell transplantation and immunotherapy. Whether hierarchical structures among stem cells at distinct niches exist and further control aspects of immune tolerance is unknown. Here we describe previously unknown new hierarchical arrangements in haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and bone marrow niches that dictate both regenerative potential and immune privilege. High-level nitric oxide-generating (NOhi) HSCs are refractory to immune attack and exhibit delayed albeit robust long-term reconstitution. Such highly immune-privileged, primitive NOhi HSCs co-localize with distinctive capillaries characterized by primary ciliated endothelium and high levels of the immune-checkpoint molecule CD200. These capillaries regulate the regenerative functions of NOhi HSCs through the ciliary protein IFT20 together with CD200, endothelial nitric oxide synthase and autophagy signals, which further mediate immunoprotection. Notably, previously described niche constituents, sinusoidal cells and type-H vessels co-localize with less immune-privileged and less potent NOlow HSCs. Together, we identify highly immune-privileged, late-rising primitive HSCs and characterize their immunoprotective niches comprising specialized vascular domains. Our results indicate that the niche orchestrates hierarchy in stem cells and immune tolerance, and highlight future immunotherapeutic targets.
European heart journal open
[IF=38.1]

文獻(xiàn)引用產(chǎn)品:
bs-1756R | Elastin Rabbit pAb | IF
作者單位:以色列哈達(dá)薩希伯來大學(xué)醫(yī)學(xué)中心
摘要:Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) is a very common cardiac valvular disorder that occurs in 2.4% of the general population. Mitral valve prolapse is characterized by the displacement of one or both leaflets towards the left atrium during valvular closure during systole. Myxomatous alteration in the valvular tissue, changes in collagen organization, and an increase in glycosaminoglycans lead to biomechanically inferior valvular tissue that results in prolapse of the mitral leaflets into the left atrium. Prolapse of the leaflets may cause progressive degeneration and leakage, and therefore, MVP is a leading indication for mitral valve surgery. Mitral valve prolapse can be complicated by infective endocarditis, valvular regurgitation, and congestive heart failure. In addition, several recent studies have demonstrated an association between MVP and ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. Dysregulation of the extracellular matrix (ECM) components plays a key role in mediating these changes and is essential for understanding the genetic pathways causing the disease.
Mitral valve prolapse is classified as non-syndromic or syndromic. Non-syndromic MVP can be familial or sporadic. Syndromic MVP occurs in association with connective tissue disorders such as Marfan syndrome (MFS), Loeys–Dietz syndrome, Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, osteogenesis imperfecta, pseudoxanthoma elasticum, and aneurysm–osteoarthritis syndrome. Familial studies of idiopathic or non-syndromic MVP suggest an autosomal dominant model of inheritance with age-dependent incomplete penetrance....
Nature Biotechnology [IF=33.1]
文獻(xiàn)引用產(chǎn)品:
bs-1356R | Integrin Alpha V + Beta 5 Rabbit pAb | IF
作者單位:慕尼黑亥姆霍茲中心智能生物技術(shù)研究所
摘要:Efficient and accurate nanocarrier development for targeted drug delivery is hindered by a lack of methods to analyze its cell-level biodistribution across whole organisms. Here we present Single Cell Precision Nanocarrier Identification (SCP-Nano), an integrated experimental and deep learning pipeline to comprehensively quantify the targeting of nanocarriers throughout the whole mouse body at single-cell resolution. SCP-Nano reveals the tissue distribution patterns of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) after different injection routes at doses as low as 0.0005?mg?kg?1—far below the detection limits of conventional whole body imaging techniques. We demonstrate that intramuscularly injected LNPs carrying SARS-CoV-2 spike mRNA reach heart tissue, leading to proteome changes, suggesting immune activation and blood vessel damage. SCP-Nano generalizes to various types of nanocarriers, including liposomes, polyplexes, DNA origami and adeno-associated viruses (AAVs), revealing that an AAV2 variant transduces adipocytes throughout the body. SCP-Nano enables comprehensive three-dimensional mapping of nanocarrier distribution throughout mouse bodies with high sensitivity and should accelerate the development of precise and safe nanocarrier-based therapeutics.
Molecular Cancer [IF=27.7]

文獻(xiàn)引用產(chǎn)品:
bs-10900R | GAPDH Rabbit pAb, Loading Control | WB
作者單位:廣州中醫(yī)藥大學(xué)附屬第一醫(yī)院
摘要:The high mortality rate from hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is due primarily to challenges in early diagnosis and the development of drug resistance in advanced stages. Many first-line chemotherapeutic drugs induce ferroptosis, a form of programmed cell death dependent on ferrous iron-mediated oxidative stress, suggesting that drug resistance and ensuing tumor progression may in part stem from reduced ferroptosis. Since circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been shown to influence tumor development, we examined whether specific circRNAs may regulate drug-induced ferroptosis in HCC. Through circRNA sequencing, we identified a novel hsa_circ_0000195 (circTTC13) that is overexpressed in HCC tissues. This overexpression is linked to higher tumor grade, more advanced tumor stage, decreased ferroptosis, and poorer overall survival. Overexpression of CircTTC13 in HCC cell lines and explant tumors was associated with increased proliferation rates, enhanced metastatic capacity, and resistance to sorafenib, while also inhibiting ferroptosis. Conversely, circTTC13 silencing reduced malignant characteristics and promoted ferroptosis. In silico analysis, luciferase assays, and fluorescence in situ hybridization collectively demonstrated that circTTC13 directly targets and reduces miR-513a-5p expression, which in turn leads to the upregulation of the negative ferroptosis regulator SLC7A11. Moreover, the inhibition of SLC7A11 mirrored the effect of circTTC13 knockdown, whereas ferroptosis inhibition mimicked the effect of circTTC13 overexpression. Both circTTC13 and SLC7A11 were highly expressed in drug-resistant HCC cells, and circTTC13 silencing induced ferroptosis and reversed sorafenib resistance in explant tumors. These findings identify circTTC13 as a critical driver of HCC progression and resistance to drug-induced ferroptosis via upregulation of SLC7A11. The cicTTC13/miR-513a-5p/SLC7A11 axis represents a potential therapeutic target for HCC.
Molecular Cancer [IF=27.7]

文獻(xiàn)引用產(chǎn)品:
bs-10211R | FOXP3 Rabbit pAb | IHC
作者單位:南方醫(yī)科大學(xué)
摘要:Background: Intratumor-resident bacteria represent an integral component of the tumor microenvironment (TME). Microbial dysbiosis, which refers to an imbalance in the bacterial composition and bacterial metabolic activities, plays an important role in regulating breast cancer development and progression. However, the impact of specific intratumor-resident bacteria on tumor progression and their underlying mechanisms remain elusive.
Methods: 16S rDNA gene sequencing was used to analyze the cancerous and paracancerous tissues from breast cancer patients. The mouse models of bearing 4T1 cell tumors were employed to assess the influence of bacterial colonization on tumor growth. Tissue infiltration of regulatory T (Treg) cells and CD8+ T cells was evaluated through immunohistochemistry and flow cytometric analysis. Comparative metabolite profiling in mice tumors was conducted using targeted metabolomics. Differential genes of tumor cells stimulated by bacteria were analyzed by transcriptomics and validated by qPCR assay.
Advanced Composites and
Hybrid Materials [IF=23.2]

文獻(xiàn)引用產(chǎn)品:
bs-1158P | AGEs | Other作者單位:大連醫(yī)科大學(xué)附屬第二醫(yī)院
摘要:Metabolic reprogramming is fundamental to synovium remodeling with drug delivery for osteoarthritis (OA) therapy. Mitochonic acid 5-MASM7@MnTBAP nanoparticles (MM@MT NPs) with various physicochemical properties and biological activities may be developed as a supramolecular nano-drug delivering to articulus for regulating mitochondrial metabolism of synovium. This study aims to explore the feasibility, efficacy, and mechanism of MM@MT NPs, which possibly excavates a novel perspective for OA therapy. Herein, for feasibility, MM@MT NPs has been indicated to possess excellent photothermal, reactive oxygen species (ROS) response, and oxygen release performances. For efficacy, MM@MT NPs has been confirmed to promote extracellular matrix (ECM) regeneration. For mechanism, MM@MT NPs has been illustrated to restore the mitochondrial membrane potential and recover the mitochondrial dynamics, which is beneficial for maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis. Moreover, MM@MT NPs has been demonstrated to stimulate the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) in mitochondria as well as enhance antioxidant capacity and eliminate oxidative stress, which is reflected in regulating the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and ROS metabolism. Therefore, MM@MT NPs can remodel the homeostasis of mitochondria via reprogramming metabolism in synovium, which achieves the symptomatic and etiological treatments of OA.
Advanced Composites and
Hybrid Materials [IF=23.2]

文獻(xiàn)引用產(chǎn)品:
bs-0292P | Bovine Serum Albumin | Other
作者單位:中國科學(xué)院遺傳與發(fā)育生物學(xué)研究所
摘要:The development of a multifunctional therapy nanoplatform is of crucial importance to tackle the complex challenges associated with cancer. Despite significant advancements in tumor treatment, the efficacy of these traditional approaches remains insufficient. Recurrence and metastasis following tumor treatment continue to represent a significant contributor to tumor-related mortality. This paper presents an improved, facile, and relatively green fabrication of (5-mercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-ylthio) acetic acid (TMT)-coated luminescent gold nanoparticles (L-AuNP@TMT), which exhibit highly membrane-targeting capacity and superior photodynamic properties. Furthermore, in vivo tumor-bearing mouse model experiments indicated that the L-AuNP@TMT could be used as a two-photon excited nanomedicine via pyroptosis-mediated anti-tumor immunity for effectively eliminating colorectal cancer (CRC), the third most common malignancy and the second deadliest cancer, without evident toxic side effects or tumor metastasis/recurrence. According to its facile and green fabrication approach, near-infrared light-activatable highly efficient photodynamic cancer therapy, and noninvasive imaging mode, this multifunctional nanoplatform offers significant advantages over traditional monotherapy techniques, providing an alternative for the precise clinical treatment of cancer.
Cellular&Molecular
Immunology [IF=21.8]

文獻(xiàn)引用產(chǎn)品:
作者單位:中國醫(yī)學(xué)科學(xué)院基礎(chǔ)醫(yī)學(xué)研究所
摘要:T-cell receptor (TCR) γδ-expressing cells are conserved lymphocytes of innate immunity involved in first-line defense and immune surveillance. TCRγδ recognizes protein/nonprotein ligands without the help of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), especially via direct binding to protein ligands, which is dependent primarily on the δ chain complementary determining region 3 (CDR3δ). However, the mechanism of protein?antigen recognition by human γδ TCRs remains poorly defined. We hypothesize that γδ TCRs recognize self-proteins expressed ectopically on the cell membrane that are derived from intracellular components under stress. Here, we mapped 16 intercellular self-proteins among 21,000 proteins with a huProteinChip as putative ligands for Vδ1/Vδ2 TCRs, 13 for Vδ1 TCRs and 3 for Vδ2 TCRs. Functional tests confirmed that ectopic nucleolin (NCL) is a ligand for the Vδ1 TCR, whereas protein-glutamine γ-glutamyltransferase K (TGM1) is a ligand for the Vδ2 TCR. In the context of radiation exposure, the ectopic expression of intracellular proteins on the tumor cell surface is related to the increased antitumor cytotoxicity of γδ T cells both in vitro and in vivo. In conclusion, the recognition of intracellular proteins that are ectopically expressed on somatic cells by human γδ TCRs is a basic interaction mechanism that enables new types of immune pattern recognition and a novel γδ TCR-ligand-based strategy for tumor immunotherapy.
Nature Microbiology [IF=20.5]

文獻(xiàn)引用產(chǎn)品:
S0134 | Alcian Blue Stain Kit (pH 2.5) | Other
作者單位:中山大學(xué)附屬第一醫(yī)院
摘要:Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is accompanied by an altered gut microbiota but whether the latter contributes to carcinogenesis is unclear. Here we show that faecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) using stool samples from patients with HCC spontaneously initiate liver inflammation, fibrosis and dysplasia in wild-type mice, and accelerate disease progression in a mouse model of HCC. We find that HCC-FMT results in gut barrier injury and translocation of live bacteria to the liver. Metagenomic analyses and bacterial culture of liver tissues reveal enrichment of the gut pathogen Klebsiella pneumoniae in patients with HCC and mice transplanted with the HCC microbiota. Moreover, K. pneumoniae monocolonization recapitulates the effect of HCC-FMT in promoting liver inflammation and hepatocarcinogenesis. Mechanistically, K. pneumoniae surface protein PBP1B interacts with and activates TLR4 on HCC cells, leading to increased cell proliferation and activation of oncogenic signalling. Targeting gut colonization using K. oxytoca or TLR4 inhibition represses K. pneumoniae-induced HCC progression. These findings indicate a role for an altered gut microbiota in hepatocarcinogenesis.